ABB Strategy Analysis

Editor-reviewed by Ahmad Zaidi based on analysis by TransforML's proprietary AI
CEO, TransforML Platforms Inc. | Former Partner, McKinsey & Company
Strategy overview for ABB
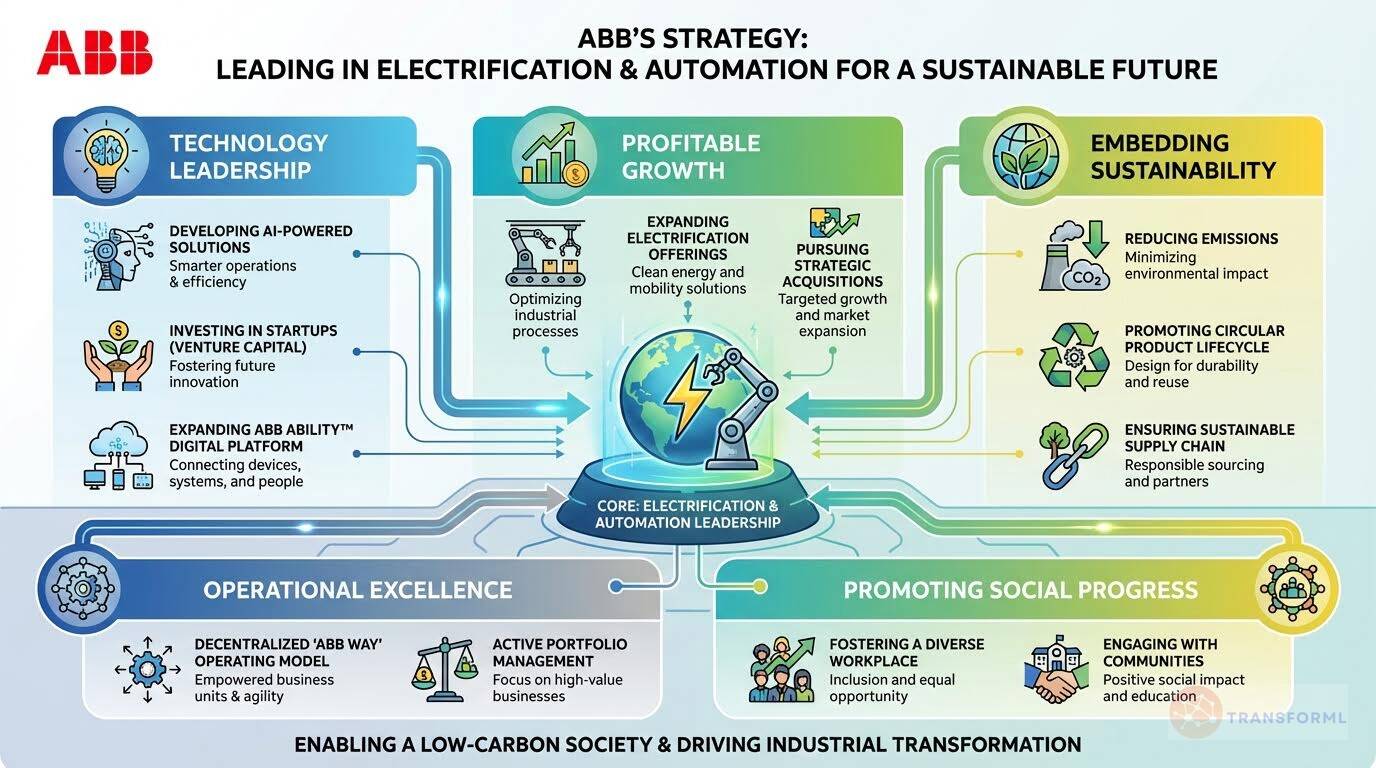
ABB's corporate strategy centers on driving profitable growth through technology leadership in electrification, automation, robotics, and digitalization, while enabling a more sustainable and resource-efficient global economy. Guided by its "Engineered to Outrun" positioning, ABB focuses on helping industrial, transportation, infrastructure, and building customers improve productivity, energy efficiency, and decarbonization outcomes. The company executes this strategy through a highly decentralized operating model known as the ABB Way, which empowers its business areas to innovate close to customers, accelerate decision-making, and deliver scalable digital solutions such as the ABB Ability platform. Strategic priorities include increased investment in R&D, selective technology-driven acquisitions, disciplined portfolio management, and embedding sustainability across products, operations, and supply chains to create long-term shareholder value and competitive advantage
Key Competitors for ABB
Siemens
Broad portfolio, strong brand recognition, established customer relationships
Schneider Electric
Focus on energy management and automation, strong presence in building automation
Rockwell Automation
Strong presence in industrial automation, focus on software and services
Emerson Electric
Diversified portfolio, strong presence in process automation
Insights from ABB's strategy and competitive advantages
What Stands Out in ABB strategy
ABB's strategy is uniquely distinguished by its sheer breadth and integrated approach, combining electrification, automation, robotics, and digitalization under a single umbrella. Unlike competitors such as Prysmian (focused on cable solutions) and PFISTERER (specializing in connection/insulation technology), ABB can offer end-to-end solutions for entire industrial ecosystems. For example, ABB can equip a factory with not only its energy-efficient electrification products but also the robotic automation and the AI-driven software (ABB Ability™ platform) to optimize the entire operation. This integrated value proposition is a significant differentiator. Furthermore, the formalized 'ABB Way' operating model, which emphasizes decentralized decision-making and accountability, is a distinct strategic capability designed to maintain agility within a large, complex organization, a feature not explicitly detailed as a core strategic driver by its competitors.
What are the challenges facing ABB to achieve their strategy
The primary challenge for ABB arises from the very breadth that defines its distinctiveness. By competing across multiple fronts, ABB faces highly focused, specialized competitors in each segment. For instance, Prysmian, as a global leader in cabling, dedicates its entire R&D and strategic focus to advancing cable technology, as seen in its 'Connect to Lead' strategy and its push for sustainable cable solutions. Similarly, PFISTERER's deep expertise in metal and silicone processing for connection technology gives it a competitive edge in its niche. ABB must ensure its individual business units can match the product innovation and market focus of these specialists. Another challenge is the inherent complexity of its business model. While the 'ABB Way' aims to mitigate this, managing and integrating such a diverse portfolio (from robotics to EV chargers) presents significant operational and strategic alignment hurdles that more focused competitors do not face. A failure or underperformance in one segment could potentially tarnish the brand's reputation across others.
What Positions ABB to win
Technology Leadership
- ABB maintains a leading position in electrification and automation technologies, supported by significant investments in R&D and a focus on digital solutions. The company's commitment to innovation enables it to develop cutting-edge products and services that address the evolving needs of its customers.
Sustainability Focus
- ABB has embedded sustainability into its core business strategy, setting ambitious targets for emissions reduction and resource efficiency. The company's commitment to enabling a low-carbon society and promoting social progress enhances its reputation and attracts environmentally conscious customers and investors.
Decentralized Operating Model
- The ABB Way empowers divisions to make decisions close to customers, fostering accountability, transparency, and speed. This decentralized model enables the company to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs, driving profitable growth and improving operational efficiency.
Strong Financial Performance
- ABB has demonstrated consistent financial performance, achieving record levels of profitability and cash flow. The company's strong balance sheet and cash generation provide the capacity and flexibility to invest in organic and acquired growth, while also rewarding shareholders through dividends and share buybacks.
Global Reach and Local Presence
- ABB has a global presence with manufacturing sites in over 40 countries, enabling it to serve customers in diverse markets. The company's local-for-local manufacturing approach allows it to remain close to customers and quickly scale innovations across its markets.
Skilled Workforce
- ABB's 110,000 employees, representing 174 nationalities, are at the core of its value creation. The company invests in employee development and training, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration.
Active Portfolio Management
- ABB actively manages its portfolio to future-proof the company by securing exposure to strong long-term market trends. This includes organic growth, portfolio adjustments, and strategic acquisitions that add technology and geographical footprint.
Strong Brand Reputation
- The ABB brand is recognized as a sign of trust, quality, and superior value for customers, partners, investors, and employees. The company's commitment to ethical business practices and responsible risk management enhances its reputation and strengthens its relationships with stakeholders.
What's the winning aspiration for ABB strategy
ABB aims to be the leading technology partner for industries seeking to enhance their productivity, efficiency, and sustainability, enabling them to 'outrun' their competition while contributing to a more sustainable and resource-efficient future.
Company Vision Statement:
We enable a more sustainable and resource-efficient future with our technology leadership in electrification and automation
Where ABB Plays Strategically
ABB competes in the electrification and automation sectors, focusing on industries undergoing energy transition and seeking improved efficiency. The company targets key markets including power generation, industry, transport, and buildings, with a global presence and a local-for-local manufacturing approach.
Key Strategic Areas:
How ABB tries to Win Strategically
ABB wins by leveraging its technology leadership, decentralized operating model, and commitment to sustainability. The company offers superior customer value through its expertise in electrification and automation, helping industries optimize, electrify, and decarbonize their operations.
Key Competitive Advantages:
Strategy Cascade for ABB
Below is a strategy cascade for ABB's strategy that has been formed through an outside-in analysis of publicly available data. Scroll down below the graphic to click on the arrows to expand each strategic pillar and see more details:
Related industry articles:
Drive Profitable Growth
Achieve sustainable and profitable growth through organic investments, strategic acquisitions, and capitalizing on market trends.
Increase R&D Investment
Increase investment in research and development to between 4.5% and 5% of revenues to foster innovation and technology leadership.
Accelerate Strategic Acquisitions
Actively pursue strategic acquisitions to add 1-2% of revenues on average through the economic cycle, focusing on technology and geographical footprint expansion.
Expand Electrification Offerings
Capitalize on the trend towards electrification by expanding offerings in electrical infrastructure, decarbonization of industries, and energy efficiency.
Enhance Automation Solutions
Capitalize on the growing demand for automation by developing and deploying automation, robotics, and AI-driven software solutions.
Maintain Technology Leadership
Sustain market leadership through cutting-edge technology, innovation, and strategic partnerships.
Develop AI-Powered Solutions
Incorporate generative AI into offerings and business processes to improve energy and resource efficiency and productivity.
Foster University Collaborations
Collaborate with universities and research institutions to build research networks and foster new technologies.
Invest in Venture Capital
Acquire minority stakes in promising start-ups, especially in specialized software and AI, to enhance the R&D ecosystem.
Expand Digital Platform
Enhance the ABB Ability™ platform with advanced software applications and digital solutions to optimize energy production and use, assets, and processes.
Embed Sustainability
Integrate sustainability into all aspects of the business, from operations to product development, and contribute to a low-carbon society.
Reduce Scope 1 and 2 Emissions
Implement measures to reduce scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by at least 80% by 2030 compared to 2019, including switching to renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency.
Reduce Scope 3 Emissions
Collaborate with suppliers to reduce scope 3 GHG emissions by 25% by 2030 compared to 2022, focusing on lower-carbon transport options and materials.
Promote Circularity Approach
Cover at least 80% of ABB's portfolio of products and solutions with the Circularity Approach by 2030, focusing on design, sourcing, and end-of-life management.
Develop Energy-Efficient Products
Develop and promote energy-efficient solutions, such as variable speed drives and high-efficiency motors, to optimize energy use and reduce waste.
Expand Sustainable Supply Base Management
Cover at least 80% of supply spending in focus countries with Sustainable Supply Base Management (SSBM) by 2030, focusing on high-risk suppliers.
Enhance Operational Excellence
Drive efficiency, accountability, transparency, and speed through the ABB Way operating model.
Deepen ABB Way Implementation
Extend the ABB Way operating model further into business lines to increase accountability, transparency, and speed of operations.
Strengthen Performance Management
Translate strategic, financial, and sustainability priorities into distinct targets, supported by appropriate incentives through the Annual Incentive Plan (AIP) and Long-Term Incentive Plan (LTIP).
Optimize Capital Allocation
Focus on funding organic growth, paying a rising and sustainable dividend, and pursuing value-creating acquisitions.
Improve Risk Management
Continuously monitor risks and opportunities to identify key factors that could affect business, growth, and strategy, and implement appropriate responses.
Reward Shareholders
Create sustainable long-term shareholder value through dividends and share buybacks.
Maintain Rising Dividend
Adhere to the policy of paying a rising, sustainable dividend per share over time.
Execute Share Buybacks
Distribute excess cash to shareholders via share buybacks, depending on M&A activity.
Fund Organic Growth
Prioritize funding organic growth, R&D, and CapEx at attractive returns to drive long-term value creation.
Manage Portfolio Actively
Continuously assess and adjust the business portfolio to ensure alignment with strategic priorities and market trends.
Conduct Portfolio Reviews
Regularly review divisions' performance and strategic mandates from a Group perspective to identify areas for improvement and potential divestments.
Pursue Strategic Acquisitions
Actively pursue acquisitions in divisions with a growth mandate to fill gaps in technology, expand market reach, and enhance economies of scale.
Divest Non-Core Businesses
Divest businesses where ABB is not the best owner to optimize the portfolio and focus on core strategic areas.
Integrate Acquired Businesses
Ensure successful integration of acquired businesses to realize synergies and achieve strategic objectives.
Promote Social Progress
Foster a diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplace while supporting communities and upholding human rights.
Reduce Lost-Time Injuries
Implement measures to achieve zero harm to employees and contractors, aiming for a gradual reduction in lost-time injury frequency rate (LTIFR).
Increase Women in Management
Increase the proportion of women in senior management roles to 25% by 2030 through targeted development activities and inclusive policies.
Improve Employee Engagement
Achieve a top-tier employee engagement score through initiatives that foster a sense of belonging and empower employees to contribute their unique perspectives.
Expand Community Engagement
Expand programs for community engagement, focusing on education, emergency relief, empowering communities, and environmental conservation.
Enhance Human Rights Due Diligence
Strengthen human rights due diligence across ABB's value chain, implementing the Human Rights Due Diligence (HRDD) Framework and providing training to employees and suppliers.
Read more about industry strategies
Source and Disclaimer: This analysis is based on analysis of Annual reports for 2024. For informational purposes only (not investment, legal, or professional advice). Provided 'as is' without warranties. Trademarks and company names belong to their respective owners.