Editor-reviewed by Ahmad Zaidi based on analysis by TransforML's proprietary AI
CEO, TransforML Platforms Inc. | Former Partner, McKinsey & Company
Oracle vs. IBM: Who is leading the race to integrate Generative AI into enterprise databases for better business insights?
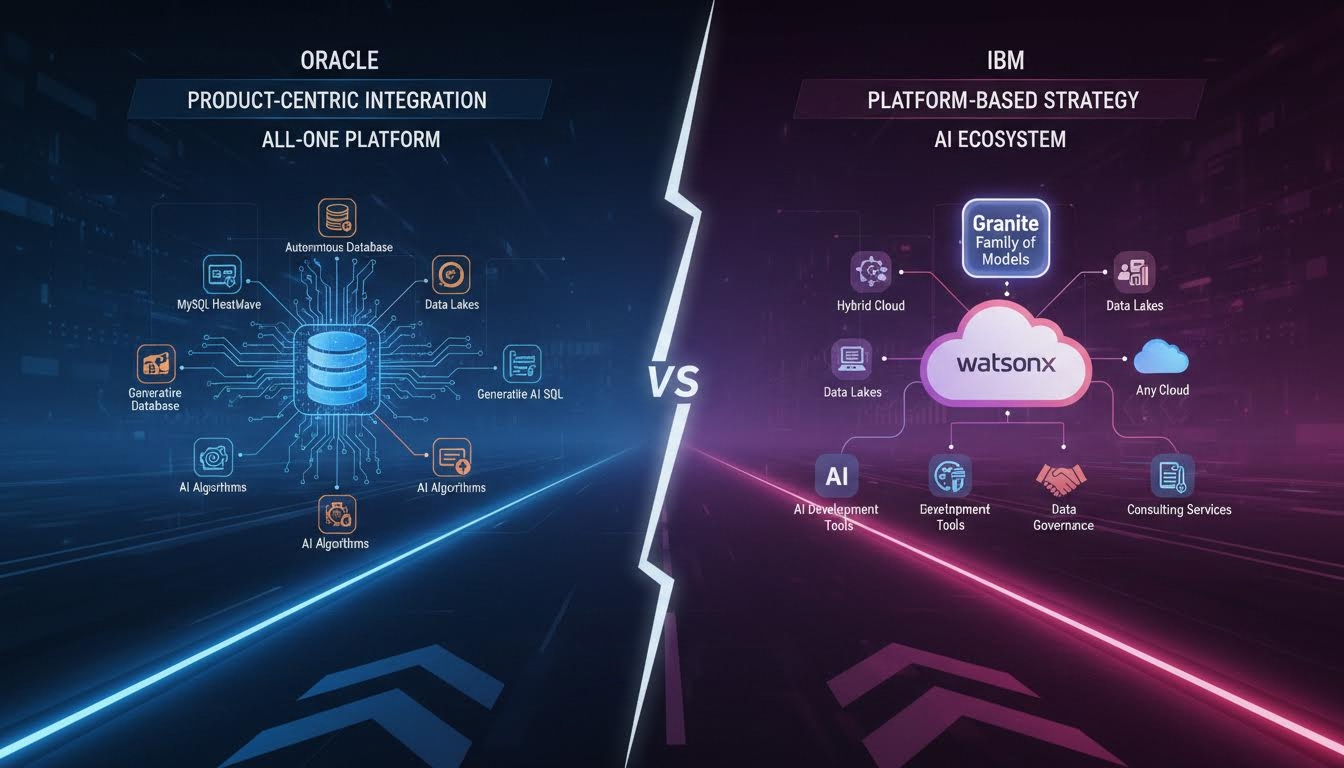
Oracle is taking a deeply integrated, product-centric approach by embedding Generative AI capabilities directly into its database offerings. A key initiative is to "Promote Oracle MySQL HeatWave Adoption" by showcasing its ability to combine transactions, real-time analytics, machine learning, and generative AI within a single managed service. This strategy aims to simplify the data architecture for customers, allowing them to run AI workloads directly on their operational data without needing to move it to a separate system. Oracle's goal is to make the database itself "smarter" and more capable, turning products like the Autonomous Database and MySQL HeatWave into all-in-one platforms for data and AI.
IBM is leading with a broader, platform-based strategy focused on empowering enterprises to build and deploy their own AI. The foundation of its strategy is "AI and Hybrid Cloud," supported by its watsonx platform and the "Granite Family of AI Models." Instead of focusing solely on the database layer, IBM provides a comprehensive AI development and governance toolkit (watsonx) that runs on its Red Hat OpenShift platform across any cloud. While Oracle is building AI into its database, IBM is building an AI platform that works with data wherever it resides. IBM's distinct "How to Win" leverages its consulting arm, which "fuels approximately 80% of IBM's AI bookings," to help enterprises implement these custom AI solutions.
Review detailed strategy and competitive analysis of companies in Database Platforms
International Business Machines Corporation
Industry: Technology
Analysis Year: 2024
Source and Disclaimer: This article is based on publicly available information and research. For informational purposes only (not investment, legal, or professional advice). Provided 'as is' without warranties. Trademarks and company names belong to their respective owners.