What strategies are companies in Medical-Device Makers using to win
Explore Medical-Device Makers company strategies

Editor-reviewed by Ahmad Zaidi based on analysis by TransforML's proprietary AI
CEO, TransforML Platforms Inc. | Former Partner, McKinsey & Company
In Medical-Device Makers, the following strategies are implemented by companies to win:
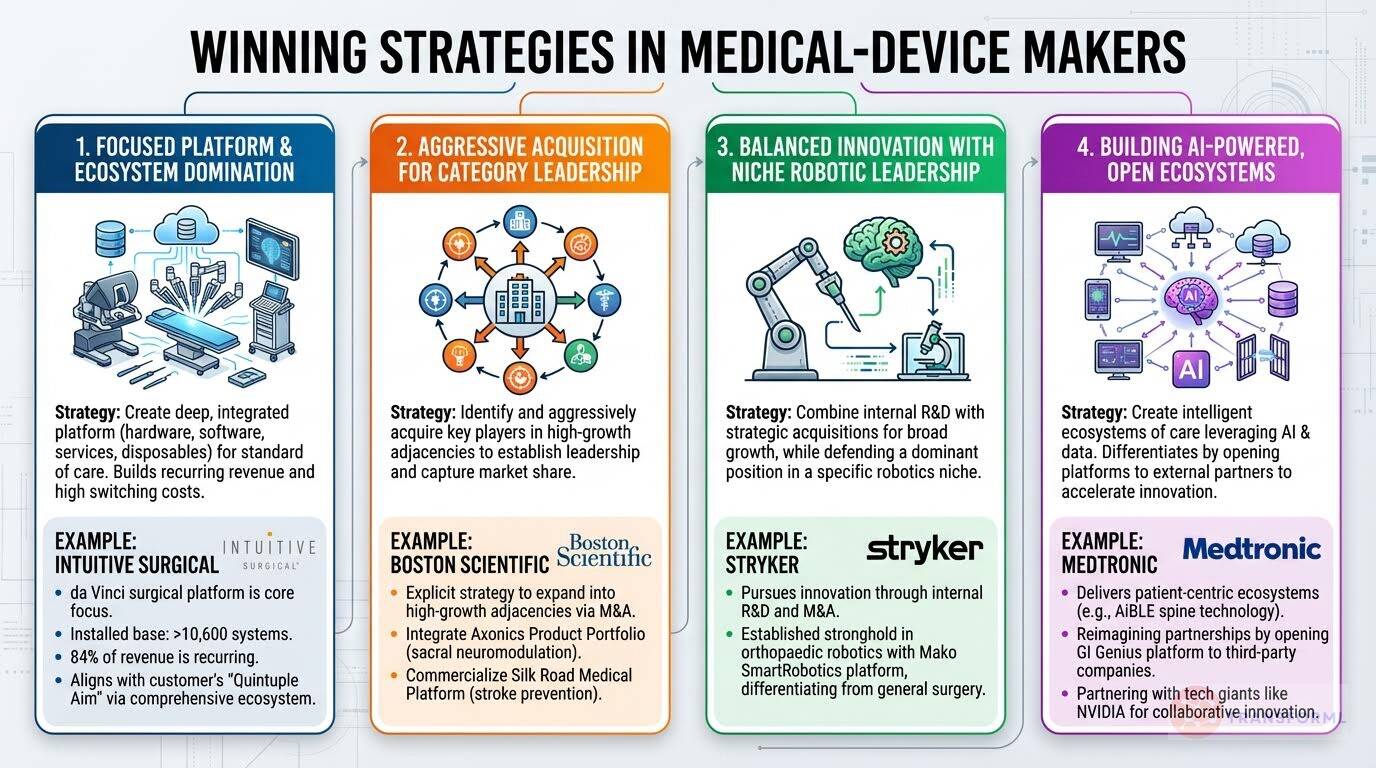
1. Focused Platform and Ecosystem Domination
This strategy involves creating a deep, integrated platform (hardware, software, services, and disposables) that becomes the standard of care in a specific domain. This builds a powerful recurring revenue model and high customer switching costs.
Example: Example: Intuitive Surgical, Inc.
Example: Intuitive's entire strategy is built around its da Vinci surgical platform. This focus has resulted in a massive installed base of over 10,600 systems and a business model where 84% of total revenue is recurring.
Example: The company wins by creating a "Comprehensive ecosystem" and aligning with the customer's "Quintuple Aim," which deepens its partnership role beyond that of a simple vendor.
2. Aggressive Acquisition for Category Leadership
This strategy focuses on identifying high-growth markets adjacent to the company's core business and then aggressively acquiring key players to quickly establish a leadership position and capture market share.
Example: Example: Boston Scientific
Example: Boston Scientific's strategy is to "Expand into High-Growth Adjacencies" and "Strengthen Category Leadership" explicitly through M&A.
Example: Key initiatives like "Integrate Axonics Product Portfolio" (for sacral neuromodulation) and "Commercialize Silk Road Medical Platform" (for stroke prevention) are direct results of this acquisition-led approach to entering and dominating new categories.
3. Balanced Innovation with Niche Robotic Leadership
This is a hybrid strategy that combines strong internal R&D with strategic acquisitions to drive growth across a broad portfolio. Critically, it also involves carving out and defending a dominant position in a specific, high-volume robotics niche.
Example: Example: Stryker
Example: Stryker's "Healthcare innovation" goal is pursued through both "Internal Research and Development" and "Strategic Mergers and Acquisitions."
Example: While competing across MedSurg and Neurotechnology, Stryker has established a clear stronghold in orthopaedic robotics with its Mako SmartRobotics platform, differentiating it from competitors focused on general surgery or spine.
4. Building AI-Powered, Open Ecosystems
This forward-looking strategy moves beyond selling individual devices to creating comprehensive, intelligent ecosystems of care that leverage AI and data. A key differentiator is opening these platforms to external partners and developers to accelerate innovation.
Example: Example: Medtronic
Example: Medtronic is explicitly "Going beyond devices to deliver patient-centric solutions and ecosystems of care," such as its AiBLE spine technology ecosystem.
Example: Its strategy of "Reimagining partnerships" is unique, demonstrated by its plan to "Open the GI Genius platform to third-party companies" and partner with tech giants like NVIDIA, transforming a device into a collaborative innovation hub.
Read More
Review detailed strategy and competitive analysis of companies in Medical-Device Makers
Source and Disclaimer: This analysis is based on publicly available industry reports, market data, and company filings. For informational purposes only (not investment, legal, or professional advice). Provided 'as is' without warranties. Trademarks and company names belong to their respective owners.